Mun Yee Koh 1, Tae-Hoon Chung 1, Nicole Xin Ning Tang 1, Sabrina Hui Min Toh 1, Jianbiao Zhou 1, Tze King Tan 1, Leilei Chen 1,2, Wee Joo Chng 1, 3, 4, Phaik Ju Teo 1, 3, 5
Affiliations
1. Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore.
2. Department of Anatomy, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore.
3. Department of Medicine, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore.
4. Department of Hematology-Oncology, National University Cancer Institute, National University Health System, Singapore, Singapore.
5. Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Abstract
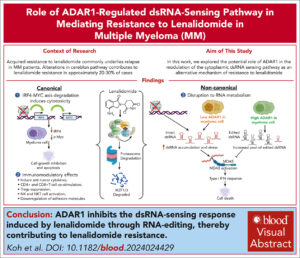
Immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) are a major class of drugs for treating multiple myeloma (MM); however, acquired resistance to IMiDs remains a significant clinical challenge. Although alterations in cereblon and its pathway are known to contribute to IMiD resistance, they account for only 20% to 30% of cases, and the underlying mechanisms in the majority of the resistance cases remain unclear. Here, we identified adenosine deaminase acting on RNA1 (ADAR1) as a novel driver of lenalidomide resistance in MM. We showed that lenalidomide activates the MDA5-mediated double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)–sensing pathway in MM cells, leading to interferon (IFN)-mediated apoptosis, with ADAR1 as the key regulator. Mechanistically, ADAR1 loss increased lenalidomide sensitivity through endogenous dsRNA accumulation, which in turn triggered dsRNA-sensing pathways and enhanced IFN responses. Conversely, ADAR1 overexpression reduced lenalidomide sensitivity, attributed to increased RNA editing frequency, reduced dsRNA accumulation, and suppression of the dsRNA-sensing pathways. In summary, we report the involvement of ADAR1-regulated dsRNA sensing in modulating lenalidomide sensitivity in MM. These findings highlight a novel RNA-related mechanism underlying lenalidomide resistance and underscore the potential of targeting ADAR1 as a novel therapeutic strategy.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2024024429

